Peter Hübner
Developer of the University
Medical Music
Preparations on CD
| . | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reducing Anxiety during Labor in Women with an Initial Inactivity of Uterine Contractility | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Already normal labor is accompanied by physical and emotional stress as well as great anxieties. This is
even more so the case when complications arise as in the investigated women here who showed an initial inactivity
of the uterus. Seen from the angle of the hormone state the organism is in a state of emergency: to counteract
the experience of great pain and severe stress for the mother, the organism produces 8-10 times more opioids
as normal, which – next to other effects – function as anxiety inhibitors. |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
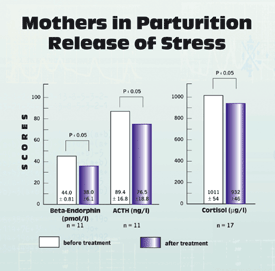
| To find out in how far Medical Resonance Therapy Music® has a harmonizing effect on anxiety regulating neuroendocrine functions important opioids were chosen for investigation: beta-endorphin, corticotropin (ACTH) and cortisol – hormones which show extremely high levels in blood during labor. | Under investigation were three groups: one group (11 women) was treated with relaxing Medical Resonance Therapy
Music, a control group A (11 women) listened to music of Mozart – Symphony No. 28 and Coronation Mass – and
a control group B (11 women) did not listen to any music at all. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Medical Resonance Therapy Music® Group | Control Group A with Mozart's Music | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The treatment with the Medical Resonance Therapy Music® resulted in a significant change of the hormonal situation:
Especially noteworthy is the following situation:
|
The women in this group also reported of a strong reduction of anxiety through listening to the music. And here too a significant change was found in the hormonal situation, but in the opposite direction: the ACTH level increased – the already hyperactive hormone system got even more exaggerated and produced even more of the anxiety inhibiting hormone. The increase of the ACTH level could explain the reduced experience of anxiety in this group.
Here no significant changes were observed, only small variations. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Comments to Cortisol
A significant change of cortisol was neither found in the “Mozart group“ nor in the Medical Resonance
Therapy Music® group. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Investigators:
Prof. Dr. med. G. Gerassimowitsch |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| DEUTSCHE FORSCHUNGSAKADEMIE DER SAKRALEN MUSIK |
| DEUTSCHE FORSCHUNGSAKADEMIE DER SAKRALEN MUSIK |
| SCIENTIFICALLY INTRODUCING UNIVERSALITY TO ACADEMIC LIFE |
| Faculties: Music & Musicology · Philosophy · Medical Sciences · Education · Pythagoras · Consciousness · Humanities · Natural Science · The Dragon · The Veda · Culture · Opera & Arts |
| . |
. | .Deutsche Übersetzung in Arbeit |
| peter huebner • micro music laboratories |
| M E D I C A L R E S O N A N C E T H E R A P Y M U S I C ® |
| R E D U C T I O N O F P S Y C H O – P H Y S I O L O G I C A L M A N I F E S T A T I O N S O F S T R E S S |