Peter Hübner
Developer of the University
Medical Music
Preparations on CD
| . | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normalization of Hemodynamic Parameters in Children with Autonomic Nervous System Disturbances | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The present investigation is dedicated to the effects of the Medical Resonance Therapy Music® on basic hemodynamic parameter in children with transient arterial hypertension due to disturbances of the autonomic nervous system with different degrees of initial sympatheticotonia.
After the nuclear accident of Chernobyl many children developed a blood pressure too high for their age norm.
Having already observed a decrease in too high blood pressure in women during pregnancy we studied the effects
of the Medical Resonance Therapy Music® (MRT-Music) on such children – with very positive results: Patients and methods Under investigation were sixty children with different degrees of initial sympatheticotonia in the children's hospital No. 3 in Minsk. Two groups were examined: one group of 32 children with an absolute sympatheticotonia, in which 75%-100% of the initial autonomic tonus were built by the sympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), and a second group of 28 children with a relative sympatheticotonia, in which 50%-75% of the initial autonomic tonus were build by the sympathetic part of the ANS. The initial tonus of the ANS was determined according to the index of Wein. |
The MRT-Music® treatments were performed twice a day at fixed times for three weeks. Before and after the treatment the following basic hemodynamic parameters were measured:
These measurements were taken using sympathomanometer according to the Korotkov method under consideration of the recommendations of the World Health Organization (1986). Other parameters under consideration were the minute volume of blood circulation (mvbc), the index of vegetative equivalence according to Hildebrandt (ih) as well as the vegetative index according to Kerdo (kerdo). The treatments were given according to the recommendations of Wein for the investigation of the autonomic nervous system. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
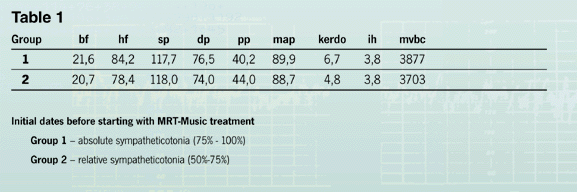
Results The investigations showed the following differences in the initial state of the organisms of the children: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The children of the first group showed higher parameters in breath and heart frequency as well as in diastolic
and mean arterial pressure than the children in the second group, but they showed lower values in the systolic
pressure, |
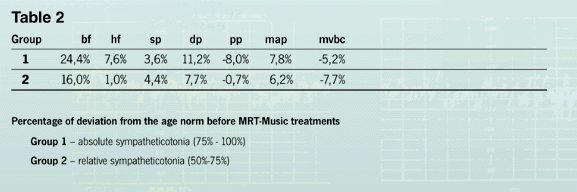
and pulse pressure and the minute volume of blood circulation. Analogue equivalences became even more clear by the analysis of the age norm which was calculated individually for each child. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
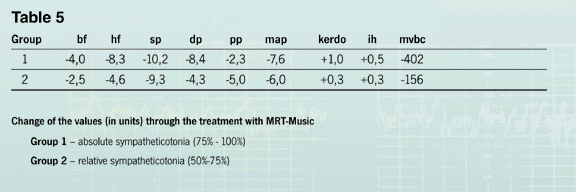
Differences in the values of the initial state correlate fundamentally differently after MRT-Music® treatment
. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
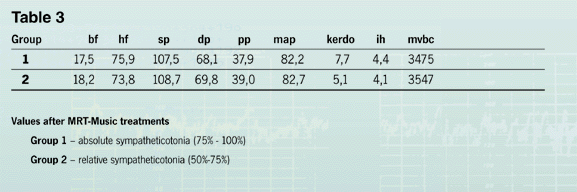
Table 3 shows that breath frequency, systolic and diastolic arterial pressure in the children of the first
group was lower than in the second group. Heart frequency and mean arterial pressure had balanced, the minute
volume of blood circulation had lowered very significantly, the Hildebrandt index had normalized. |
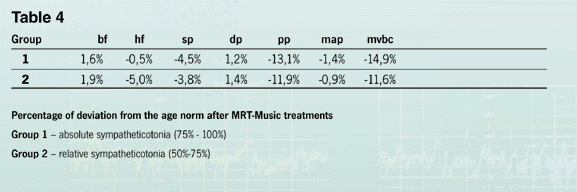
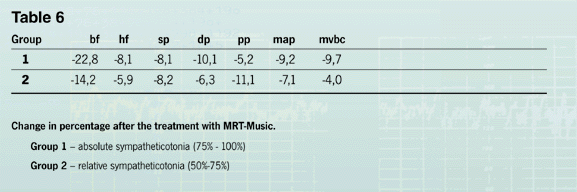
Analysation of the deviation from the age norm (see table 4) shows, that in both groups breath frequency,
heart frequency, systolic, diastolic and mean arterial pressure assimilated and pulse pressure and minute
volume of blood circulation stayed below the average age norm, but without falling below the healthy limits. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
In comparing the effects of the MRT-Music® treatments the greater changes in the group with absolute sympatheticotonia
were evident, which may be explained by the normalization of |
the initially to high values. Remarkable is that after the MRT-Music® treatments the parameters of the vegetative
balance and of the inter-systemic relations practically stay the same. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Conclusions
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Investigators:
Dr. med. J. J. Komlikow |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| DEUTSCHE FORSCHUNGSAKADEMIE DER SAKRALEN MUSIK |
| DEUTSCHE FORSCHUNGSAKADEMIE DER SAKRALEN MUSIK |
| SCIENTIFICALLY INTRODUCING UNIVERSALITY TO ACADEMIC LIFE |
| Faculties: Music & Musicology · Philosophy · Medical Sciences · Education · Pythagoras · Consciousness · Humanities · Natural Science · The Dragon · The Veda · Culture · Opera & Arts |
| . |
. | .Deutsche Übersetzung in Arbeit |
| peter huebner • micro music laboratories |
| M E D I C A L R E S O N A N C E T H E R A P Y M U S I C ® |
| R E D U C T I O N O F P S Y C H O – P H Y S I O L O G I C A L M A N I F E S T A T I O N S O F S T R E S S |